Charismatic megafauna is the mouthful of a phrase used to describe the big lovable beasts the world wants to save – or at least cast as stars of our cartoons.
Two recent setbacks with saltwater giants illustrate how being big and adored doesn't always get the job done.
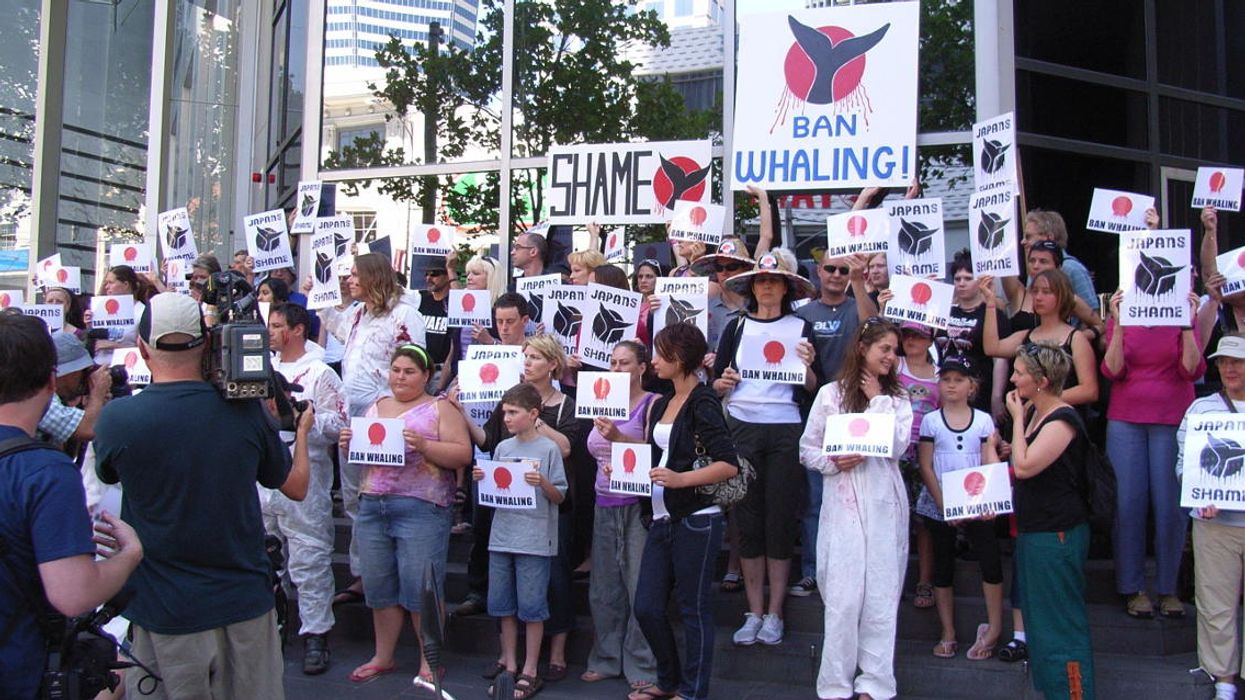
Compared to other more daunting environmental challenges, ending commercial whaling was thought to be easy. The industry was already on its heels due to lack of demand, not to mention, lack of whales.
Global public opinion helped chase whalers out of all but a few nations. And the conservation movement focused its strength on ending commercial whaling everywhere to seal what seemed a major victory.
In 1984, a ban on commercial whaling took effect, over the objections of Japan, Norway and Iceland. With a few exceptions for subsistence whaling by native communities, whaling was dead.
Or so we thought.
Almost immediately, Japan's whaling fleet leveraged a loophole in the International Whaling Commission's decree, allowing for limited whaling to continue for scientific "research."
Hundreds of whales per year, mainly minke whales, gave their lives for this research, the premise of which was so shabby that opponents described it as "more sushi than science."
Whale meat found its way to Japanese markets, just like in the good old days.
Norway and Iceland chipped in and whaling hung on, albeit at far lower levels. Last month, Japan announced it was quitting the IWC after decades of battling its decisions.
Instead of steaming to the Antarctic, their fleet will stay close to home to kill minkes and two other species, Bryde's and Sei whales.

Frozen Bluefin Tuna ready for auction at Tsukiji Market in Tokyo. (Credit: Matt Saunders/flickr)
Similarly, much has been written about the bluefin tuna, a half-ton torpedo of a fish whose value has skyrocketed as its numbers have plummeted. Again, Japan is the eco-villain.
In December, a single bluefin sold in Tokyo for $3.1 million – a perverse free-market incentive to catch the last one. The fish, relatively small at 612 pounds, was one more withdrawal from a Pacific bluefin stock estimated to be 96 percent down from its original population.
And if our global imagination isn't stoked by saving big fish, and even bigger whales, what about more ephemeral challenges like rising CO2 levels? In 2017 and again last year, our output of the dominant greenhouse gas increased, despite the torrent of warnings about our climate death wish.
I wrote a few weeks ago about the Antarctic Treaty and Montreal Protocol, two international agreements that succeeded in protecting a frozen continent and the ozone layer.
They're examples of how international cooperation can work. But if we can't come together on protecting charismatic megafauna, or even achieving modest gains in CO2 reduction, they're examples of the tough battles ahead.